CRM Software for Small Business Success
CRM Software for Small Business: Unlocking growth and efficiency is easier than you think. Choosing the right Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system can significantly impact a small business’s ability to manage leads, nurture relationships, and ultimately, boost profitability. This guide explores the essential aspects of selecting, implementing, and optimizing a CRM solution tailored to the unique needs of small businesses, regardless of industry.
From defining your specific requirements and exploring various software options to mastering implementation and measuring success, we’ll equip you with the knowledge to make informed decisions and maximize your return on investment. We’ll delve into practical strategies for overcoming common challenges and ensuring your CRM system becomes a valuable asset rather than a costly burden.
Defining Needs for Small Business CRM
Choosing the right CRM (Customer Relationship Management) system is crucial for small businesses aiming to streamline operations and boost growth. A well-implemented CRM can centralize customer information, improve communication, and ultimately drive sales. Understanding your specific needs is the first step towards selecting the optimal solution.
Core Functionalities for Small Business CRM
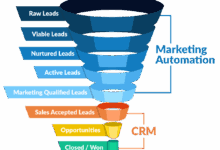
Small businesses require a CRM that balances ease of use with essential features. Core functionalities typically include contact management (with the ability to store customer details, interaction history, and notes), lead management (tracking potential customers from initial contact to conversion), sales pipeline management (visualizing the sales process and identifying bottlenecks), and basic reporting (providing insights into sales performance, customer behavior, and marketing campaign effectiveness). Additional beneficial features might include appointment scheduling, task management, and email integration.
CRM Requirements Across Different Small Business Types
The specific CRM needs vary depending on the business type. Retail businesses, for example, might prioritize inventory management integration, point-of-sale (POS) system integration, and customer segmentation for targeted marketing campaigns. Service businesses, such as plumbers or hair salons, will likely focus on appointment scheduling, service history tracking, and customer feedback management. Consulting firms, on the other hand, may emphasize project management features, client relationship tracking, and time tracking capabilities. While all these businesses benefit from core CRM functions, their priorities and feature needs diverge significantly.
Scalability and Future-Proofing in CRM Selection
Choosing a scalable CRM is paramount for long-term success. A system that can adapt to your growing business needs avoids the costly and disruptive process of switching platforms later. Consider factors like user capacity, data storage limits, and the availability of advanced features as your business expands. Future-proofing also involves selecting a CRM with robust API integrations, allowing for seamless connections with other business tools as your tech stack evolves. For instance, a small business starting with basic email marketing could later integrate with more sophisticated marketing automation platforms. The CRM should facilitate this growth without significant hurdles.
Comparison of CRM Features Across Pricing Tiers
The features offered by CRM systems often vary depending on the pricing tier. Below is a comparison of three common features across three hypothetical tiers (Basic, Standard, and Premium):
| Feature | Basic | Standard | Premium |
|---|---|---|---|
| Contact Management | Basic contact storage, limited custom fields | Advanced contact management, custom fields, segmentation | Advanced contact management, custom fields, segmentation, automation, integration with other platforms |
| Sales Pipeline | Simple pipeline visualization, basic reporting | Detailed pipeline visualization, advanced reporting, forecasting | Detailed pipeline visualization, advanced reporting, forecasting, sales automation, workflow automation |
| Reporting | Basic sales reports | Customizable reports, dashboards | Advanced analytics, custom dashboards, real-time reporting, predictive analytics |
Exploring CRM Software Options
Choosing the right CRM software can significantly impact a small business’s efficiency and growth. The market offers a wide variety of options, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Carefully considering your specific needs and budget is crucial before making a decision. This section will explore several popular CRM options, comparing their features and pricing models to help you make an informed choice.
Popular CRM Software Options for Small Businesses
Several CRM systems cater specifically to the needs and budgets of small businesses. These systems often offer simplified interfaces and affordable pricing plans, making them accessible to companies of all sizes. Some of the most popular choices include HubSpot CRM, Zoho CRM, Salesforce Essentials, Freshsales, and Keap (formerly Infusionsoft). Each platform offers a unique set of features and functionalities.
Detailed Descriptions of Three CRM Software Solutions
HubSpot CRM: HubSpot offers a robust, free CRM with a user-friendly interface. Its strengths lie in its comprehensive marketing automation tools, seamlessly integrating with other HubSpot products. However, its free plan has limitations, and advanced features require upgrading to a paid plan, which can become expensive as your business grows. The free version might lack certain functionalities crucial for larger operations.
Zoho CRM: Zoho CRM provides a highly customizable and scalable solution, offering a wide range of features at various price points. Its strength is its flexibility; it can adapt to different business models and workflows. However, its interface can feel overwhelming to users unfamiliar with CRM software, requiring a steeper learning curve. The sheer number of features can also lead to confusion for smaller teams.
Salesforce Essentials: Salesforce Essentials is a simplified version of the powerful Salesforce platform, tailored for small businesses. It offers core CRM functionalities like contact management, sales pipeline tracking, and basic reporting. Its strength is its integration with other Salesforce products, offering a scalable solution as your business expands. However, it can be more expensive than other options, and its features may be less extensive than those offered by some competitors at similar price points. The learning curve, though less steep than the full Salesforce platform, still exists.
Comparison of Pricing Models
Understanding the different pricing models is essential for selecting a CRM that fits your budget. Here’s a comparison of five popular CRM systems:
| CRM System | Pricing Model | Description |
|---|---|---|
| HubSpot CRM | Freemium | Offers a free plan with limited features and paid plans with increasing functionality and user capacity. |
| Zoho CRM | Subscription | Offers various subscription tiers with different feature sets and user limits, allowing for scalability. |
| Salesforce Essentials | Subscription | Subscription-based pricing with different tiers based on the number of users and features. |
| Freshsales | Subscription | Offers a range of subscription plans, from basic to enterprise-level, catering to businesses of different sizes. |
| Keap (formerly Infusionsoft) | Subscription | Primarily subscription-based, offering various plans with differing levels of features and automation capabilities. |
Feature Comparison of Five CRM Systems
The following table summarizes the key features of five popular CRM systems, categorized by functionality.
Note: Feature availability varies across different pricing tiers.
| Feature Category | HubSpot CRM | Zoho CRM | Salesforce Essentials | Freshsales | Keap |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sales | Contact management, deal tracking, sales pipeline visualization | Contact management, deal tracking, sales forecasting, lead scoring | Contact management, opportunity tracking, sales reporting | Contact management, deal tracking, sales automation | Contact management, sales pipeline management, automation |
| Marketing | Email marketing, social media integration, landing pages | Email marketing, social media integration, marketing automation | Limited marketing features; integration with other marketing tools often required | Email marketing, marketing automation, lead nurturing | Robust marketing automation, email marketing, landing pages |
| Customer Service | Basic ticketing system, integration with live chat tools | Ticketing system, knowledge base, customer support tools | Limited customer service features; integration with other support tools often required | Ticketing system, self-service portal | Ticketing system, email integration, support automation |
Implementation and Integration
Successfully implementing a CRM system requires careful planning and execution. A smooth transition minimizes disruption to daily operations and maximizes the benefits of the new system. This section details the key steps involved, from data migration to employee training.
Implementing a new CRM system in a small business involves a structured approach to ensure a smooth transition and maximize the return on investment. This process requires careful consideration of data migration, system integration, and employee training.
Data Migration Strategies
Effective data migration is crucial for a successful CRM implementation. Inaccurate or incomplete data renders the CRM system useless. The process involves extracting data from existing systems (spreadsheets, databases, etc.), cleaning and transforming it to fit the CRM’s structure, and then uploading it into the new system. This requires careful planning to minimize downtime and data loss. For example, a small bakery might migrate customer contact information, order history, and loyalty program data from a spreadsheet into their new CRM. They would need to ensure data consistency (e.g., standardizing address formats) before importing. A phased approach, starting with a small subset of data, allows for testing and correction before migrating the entire dataset. Regular backups throughout the process are essential to mitigate potential data loss.
CRM System Integration with Other Business Tools
Integrating your CRM with other business tools significantly enhances efficiency and streamlines workflows. Common integrations include email marketing platforms (Mailchimp, Constant Contact), accounting software (Xero, QuickBooks), and e-commerce platforms (Shopify, WooCommerce). For instance, integrating the CRM with an email marketing platform allows for automated email campaigns based on customer interactions within the CRM. Similarly, integration with accounting software automates invoice generation and payment tracking. The specific integration methods vary depending on the software used, often involving APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) or third-party integration tools. Successful integration requires understanding the capabilities of each system and the data flow between them. A small clothing boutique, for example, might integrate its CRM with its e-commerce platform to track customer purchases and preferences, enabling personalized marketing campaigns.
Employee Training Program
Comprehensive employee training is paramount for successful CRM adoption. A well-structured training program ensures employees understand the system’s functionalities and how to use it effectively. This typically involves a combination of methods, including online tutorials, hands-on workshops, and ongoing support. The training should cover basic navigation, data entry, reporting, and specific workflows relevant to each employee’s role. For example, sales representatives need training on managing customer interactions and sales pipelines, while customer service representatives need training on managing customer inquiries and support tickets. Regular refresher training and ongoing support are crucial for maintaining employee proficiency and addressing any emerging issues. A step-by-step guide, including screenshots and video tutorials, can enhance the training effectiveness. Providing ongoing support through dedicated staff or online resources helps employees address challenges and ensure smooth system usage.
Step-by-Step Guide for Employee Training
- Needs Assessment: Identify the specific CRM features employees need to learn based on their roles.
- Training Materials Development: Create comprehensive training materials, including manuals, videos, and interactive tutorials.
- Initial Training Sessions: Conduct initial training sessions covering basic functionalities and key workflows.
- Hands-on Practice: Provide opportunities for employees to practice using the CRM in a simulated or real-world environment.
- Ongoing Support and Refresher Training: Offer ongoing support through FAQs, online forums, or dedicated staff. Schedule regular refresher training sessions to reinforce learning and address new features.
Measuring Success and ROI
Implementing a CRM system is an investment, and understanding its effectiveness is crucial for justifying its cost and ensuring a positive return. Measuring the success of your CRM hinges on tracking relevant key performance indicators (KPIs) and calculating your return on investment (ROI). This allows for data-driven decision-making and optimization of your CRM strategy.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for CRM Effectiveness
Several key metrics provide insights into the performance of your CRM system. These indicators help businesses understand how well the CRM is supporting sales, marketing, and customer service efforts. Monitoring these KPIs allows for timely adjustments to optimize CRM usage and maximize its benefits.
| KPI | Description | Example | Measurement Method |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lead Conversion Rate | Percentage of leads that convert into customers. | Increased from 5% to 12% after CRM implementation. | (Number of converted leads / Total number of leads) * 100 |
| Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) | The cost of acquiring a new customer. | Reduced from $500 to $300 per customer. | Total marketing and sales costs / Number of new customers acquired |
| Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV) | The predicted revenue a customer will generate throughout their relationship with the business. | Increased from $1,000 to $1,500 per customer. | Average purchase value * Average purchase frequency * Average customer lifespan |
| Customer Churn Rate | Percentage of customers who stop doing business with the company within a specific period. | Decreased from 15% to 8% after implementing targeted retention strategies via the CRM. | (Number of churned customers / Total number of customers) * 100 |
Tracking Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) and Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV)
Using CRM data, businesses can accurately track CAC and CLTV. The CRM system provides a detailed record of marketing and sales activities associated with each customer acquisition, allowing for precise CAC calculation. Similarly, purchase history and customer interaction data within the CRM enable accurate CLTV prediction. The relationship between CAC and CLTV is vital; a healthy business model requires CLTV to significantly exceed CAC.
CAC = Total Marketing & Sales Costs / Number of New Customers Acquired
CLTV = Average Purchase Value * Average Purchase Frequency * Average Customer Lifespan
For example, a company spends $10,000 on marketing and acquires 50 new customers. Their CAC is $200 ($10,000 / 50). If the average customer spends $500 annually for 5 years, their CLTV is $2,500 ($500 * 5). This shows a positive relationship where CLTV (2,500) greatly exceeds CAC (200).
Calculating the Return on Investment (ROI) of a CRM System
Calculating the ROI of a CRM system involves comparing the benefits gained against the costs incurred. Benefits include increased sales, improved customer satisfaction, reduced operational costs, and enhanced efficiency. Costs include the software license, implementation fees, training, and ongoing maintenance. A positive ROI indicates a successful CRM implementation.
ROI = (Net Benefits – Total Costs) / Total Costs * 100%
For instance, if a company invests $5,000 in a CRM system and experiences a $15,000 increase in revenue due to improved sales efficiency, the net benefit is $10,000. The ROI is 200% (($10,000/$5,000) * 100%).
Dashboard Visualizing Key Metrics
A CRM dashboard provides a real-time overview of key metrics, facilitating quick identification of trends and areas needing attention. This visual representation of data enhances decision-making and allows for proactive adjustments to the CRM strategy.
| Metric | Data Source | Visualization | Actionable Insight |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lead Conversion Rate | CRM Sales Pipeline | Line graph showing conversion rate over time | Identify bottlenecks in the sales process |
| Customer Churn Rate | CRM Customer History | Bar chart comparing churn rates across different customer segments | Target at-risk customers with retention strategies |
| Average Customer Spend | CRM Transaction History | Pie chart showing customer spending distribution across product categories | Identify top-selling products and customer preferences |
| Customer Satisfaction (CSAT) Score | CRM Customer Feedback | Gauge chart displaying the current CSAT score | Identify areas for improvement in customer service |
Addressing Common Challenges
Implementing a CRM system, while beneficial, often presents hurdles for small businesses. Understanding these common challenges and proactively addressing them is crucial for successful CRM adoption and realizing its full potential. This section outlines typical obstacles and offers practical solutions for overcoming them.
Data Entry Issues and Maintaining Data Accuracy
Inconsistent or inaccurate data renders a CRM system ineffective. Data entry errors can stem from various sources, including insufficient training, cumbersome data entry processes, and a lack of clear data entry guidelines. Solutions include implementing streamlined data entry processes, using pre-filled forms, employing data validation tools to catch errors in real-time, and providing comprehensive training to staff on proper data entry procedures. Regular data cleansing and reconciliation, involving periodic checks for inconsistencies and duplicates, are also essential. For instance, implementing a system where customer data is automatically populated from other integrated systems like e-commerce platforms can drastically reduce manual entry and associated errors. Regular audits and data quality reports can highlight areas needing improvement, enabling proactive intervention.
Improving User Adoption and Engagement
Low user adoption is a significant impediment to CRM success. Resistance often arises from a lack of understanding of the system’s benefits, insufficient training, or a cumbersome user interface. To foster adoption, comprehensive and ongoing training programs are vital, coupled with readily available support resources, such as FAQs, help guides, and video tutorials. The system’s interface should be intuitive and user-friendly, minimizing the learning curve. Highlighting the CRM’s benefits through regular communication and demonstrating its value in streamlining workflows and improving efficiency can significantly boost user engagement. Incentivizing usage, such as recognizing top performers or integrating gamification elements, can also encourage active participation. For example, offering rewards for consistently using the CRM to track customer interactions could motivate staff to fully utilize its capabilities.
Ensuring Data Security and Privacy
Protecting sensitive customer data is paramount. Data breaches can severely damage a business’s reputation and lead to legal repercussions. Robust security measures are crucial, including strong passwords, access controls based on roles and responsibilities, regular software updates to patch vulnerabilities, and encryption of sensitive data both in transit and at rest. Compliance with relevant data privacy regulations, such as GDPR or CCPA, is also essential. Regular security audits and penetration testing can identify potential weaknesses before they are exploited. Furthermore, clear data privacy policies should be established and communicated to all employees, outlining their responsibilities in protecting customer data. For example, implementing multi-factor authentication and regularly backing up data to a secure offsite location can significantly enhance data security and minimize the risk of data loss.
Epilogue
Successfully implementing CRM software for your small business requires careful planning, diligent execution, and a commitment to ongoing optimization. By understanding your needs, researching available solutions, and prioritizing user adoption, you can transform your customer interactions, streamline operations, and drive sustainable growth. Remember, the right CRM isn’t just a software; it’s a strategic investment in your business’s future.